|
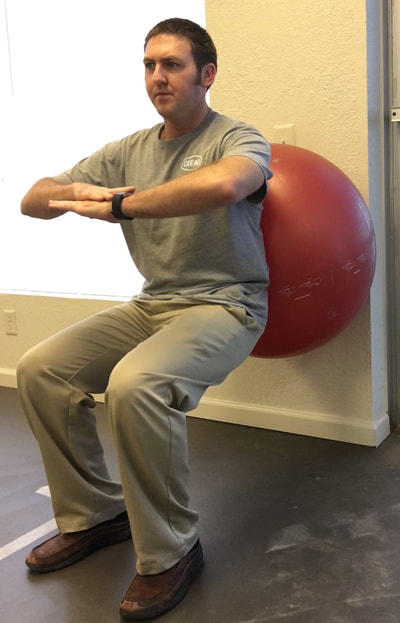
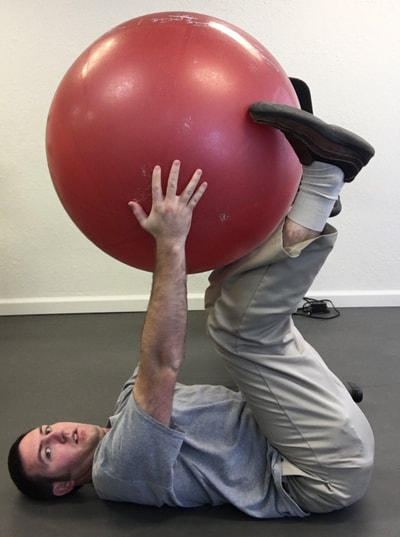
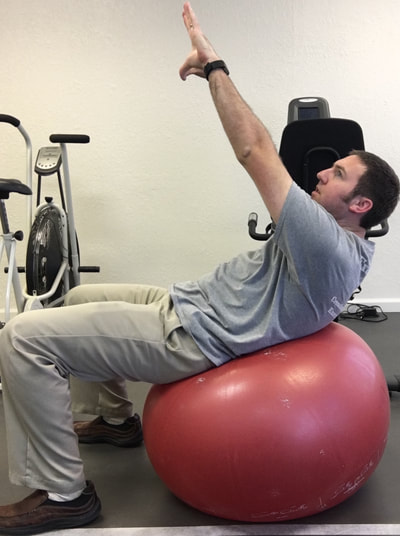
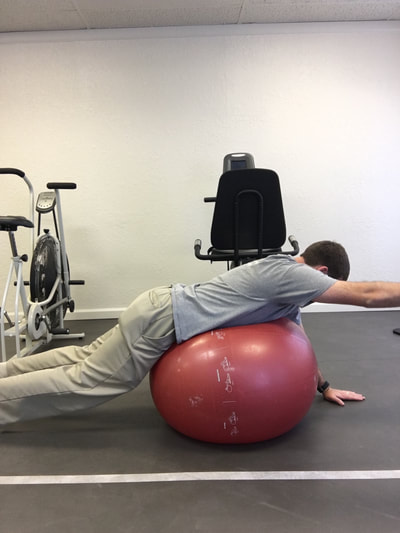
Injury prevention is something that is discussed often in the physical therapy world. Many physical therapists that work with athletes focus on this area, whether its running, or soccer, or golf, etc. Perhaps more uncommon is the idea of injury that can take place for musicians, specifically when playing a keyboard instrument such as the piano or organ. One might wonder how an injury might occur just sitting on a bench playing the piano, but in reality there are multiple ways that injury can occur while playing the piano or organ. Recently a close friend of the family who is a music teacher and who offers piano lessons brought this topic up and wrote her own blog post about this very topic. I will be the first to admit that I had never considered this in the past. Please be sure to read her post here, as I was featured as a guest on her blog. She asked some great questions about this topic and I was able to give some expert advice. In my post I would first like to highlight some of the possible injuries that can occur, as well as to provide a list of ten exercises that one could do for prevention. These would serve as a warm up prior to sitting at the bench in order to prevent injury through proper posture and adequate flexibility. So, what injuries are possible while playing a keyboard instrument? First, the wrist/hand and forearms are a potential source of problems due to development of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), ligament sprains at the wrist/digits, and even neural tension at the wrist, elbow, or shoulder (or all three) due to poor posture. Posture is a crucial aspect of injury prevention. Ideally, one should be sitting upright with feet flat on the floor (unless using pedal with right foot or playing pedals on an organ), shoulders back, and head erect with eyes relaxed looking at the keys/sheet music. The hands and wrist should be relaxed, as if sitting on top of a bubble. If this is NOT done and the individual is slouched, multiple impairments can result. Namely: shortened and tight neck muscles (can result in tension headache and compression of cervical nerve roots), increased strain of upper back and shoulder muscles (results in poor shoulder stability and lack of support for the neck), increased stress on the discs and facet joints of the lumbar spine (ligament strain of the joints of the back and possible disc bulge or rupture), shortened and tight hip flexor muscles (also results in more stress on lumbar spinal segments), etc, etc. The take away here is that posture is HUGE for preventing injuries at the piano/organ. What can be done about this, besides maintaining adequate posture? The exercises I am about to recommend will go a long way to facilitate good posture while playing, flexibility of the neck, upper limbs, and trunk, as well as to promote warming up the tissues prior to playing. Let's face it, playing a musical instrument can by physically challenging and can certainly be a form of exercising. For piano, the hands must be limber and agile to play each key and to reach octaves, etc. And if the song is a fast tempo and has a large range of notes, the entire upper limb system is getting a workout. My hands and arms are always fatigued after a long session at the piano. This is expected and perfectly natural. So, as before any workout, a warm up is essential. And no, I don't mean sitting at the piano and cracking your knuckles and your neck. Leave that for the cartoons. The last part of this post will be to highlight the exercises that will provide a well rounded warm up for injury prevention. There is a video linked to this post to see the exercises in action and then a written list below the video. Recommended Exercise Routine The following exercises are found in the video that you just saw above. If you are looking for an exercise ball and yoga mat like used in the video you can get them via the links in this post. * For the following exercises, I recommend 5-10 repetitions of each immediately prior to sitting down on the piano bench. *As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases
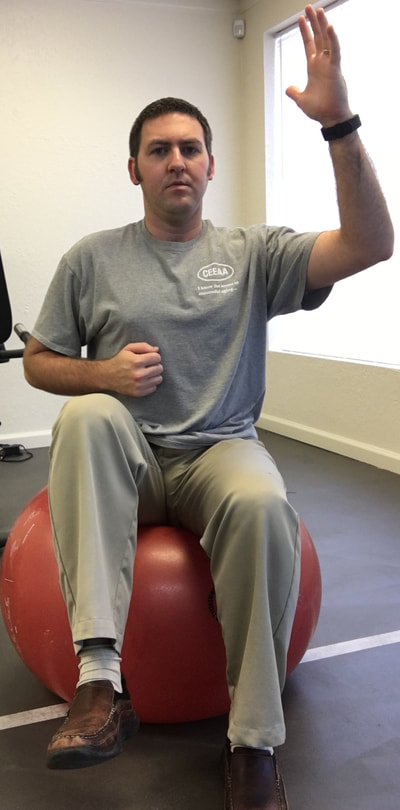
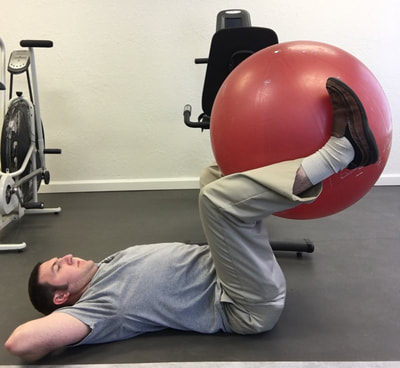
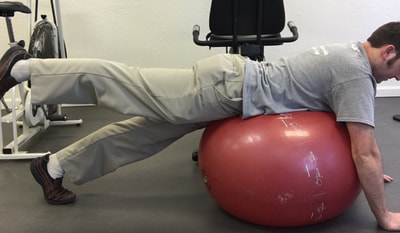
1. Standing pectoralis doorway stretch - This will help to open up the chest, stretch the pectoralis muscles, and to encourage erect posture. 2. Standing pectoralis/biceps stretch - Again, this encourages opening up the chest and bringing the shoulders and arms back. Tightness in pectoralis major and minor can result in neural tension of the brachial plexus (this is the bundle of nerves that exit the neck, under the collar bone, and into the shoulder and arm). 3. Standing upper limb prayer stretch/neural glide - This exercise moves the entire upper limb through a range of motion that encourages lengthening the nerves of the upper body through all of the bends in the limb. This is not as specific, but is a great warm up exercise. 4. Median nerve glide - This is a specific stretch for the median nerve of the upper limb. This is the culprit in carpal tunnel syndrome as the median nerve is often compressed at the wrist. 5. Radial nerve glide - Another specific stretch for the radial nerve. This supplies the sensation for the back of your hands and is the motor nerve for the muscles that extend the fingers and wrist. 6. Ulnar nerve glide - A specific stretch for the ulnar nerve. This supplies the sensation for the half of the palm near the ring and pinky fingers. This nerve can be compressed at the elbow (where your funny bone is) as well as at the wrist (Guyon's tunnel). Guitarists may need to worry about this one more than the medial nerve, but both are important to stretch for the keyboardist. 7. Cervical/neck rotation, side bending, and flexion/extension - These are combined due to the fact that they are all the same area of the spine. These are great for general flexibility for the joints of the neck while turning the head right and left, bending to the side, and looking up/down. This is important for limbering up the joints of the neck as well as warming up the muscles that will be working to hold your head up while playing. 8. Standing trunk rotation - General flexibility exercise for the upper and lower back to loosen up the joints of the spine and warm up the muscles of the trunk 9. Back extension - General flexibility exercise for the lumbar spine to encourage good sitting posture and to move the spine in the opposite direction of slouching. This can alleviate soreness in the back as well. 10. Lower trunk rotation with legs on ball - Good general flexibility exercise for the lower back muscles and joints. This can be a great one for relieving stiffness and soreness in the lower back as well. If you are looking for an exercise ball you can purchase one here.* *As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases In this case, I mean in the LITERAL sense! So, here's the thing, there are a TON of exercises that you can do with an exercise ball.* If you have worked with me as a client before, or if you plan to in the future, there are so many ways you can prescribe exercise, even a home exercise program, with a ball* such as this. Why? Well, they are light weight, relatively easy to store, and you can do so many exercises without even using weights and you will really get a workout! I thought I would put together a list of exercises that would be really useful if you obtain a therapy ball. Any of the links found in this post will take you to a ball that I recommend in particular*. The GoFit professional stability ball is the one that I use in the clinic and in my videos, because its not expensive and it even comes with printed exercises on the side to give you an extra challenge and ideas of what to do. WARNING, I would NOT start with the ones printed on the side of this particular ball. But I am going to give you even MORE ideas so you can get started now! ( Wave your mouse over images for caption). These particular exercises would be helpful for back pain. *As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases So here goes: Prone Glut Sets Bridges on ball Lower abdominal sets Ball crunches I hope you find these exercises helpful and that this gives you an idea of how you might manage back pain by obtaining a therapy ball. This one tool could save you lots of time and money due to space savings and versatility. For more information, please call me today to discuss other ideas for treating your back pain. 918-251-7199.
P.S. If you are looking for a soft spot to lay this yoga mat is the one I use and I love it because of its extra cushioning! Be empowered! *As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases 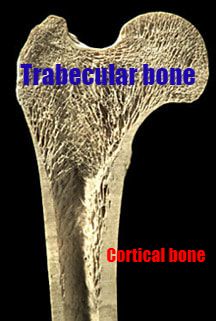 Image courtesy of ASBMR Educational Materials https://goo.gl/images/NR4gxM Image courtesy of ASBMR Educational Materials https://goo.gl/images/NR4gxM Osteoporosis (OP) is a condition effecting the bones and is associated with very low bone mineral density (BMD). The name itself means "porous bones" and results in the bones becoming brittle and leading to fractures due to bone fragility. This is typically associated with women, but men can also have the condition as sex hormones diminish over the decades. Most, if not all people with OP, started out with osteopenia (low BMD, but not yet progressed to osteoporosis). This is the best time to prevent onset of OP, but even those with OP can prevent worsening of the condition, prevent fractures, and prevent falls that lead to fractures. Osteoporosis Canada has great resources on the condition. The full list of "fast facts" can be found here, but to me one of the most profound listed is that 80% of fractures in those 50+ are due to OP. Many of these folks will not be diagnosed with OP and will not be prescribed the correct preventative treatment. Medications and supplements are very important, but exercise is a crucial medicine for OP. Why Exercise Is Important With OP Reason 1: Preserving bone density. With aging we all start to lose bone density as young as our thirties. The amount of exercise and physical activity that you challenge your body with, as well as the amount of calcium that you consume in youth, have a direct impact upon the health of your bones as you age. Think of it as a bank where you make deposits over time. The more you store up for the future, the more healthy your bones are. But again, why is exercise so important? Two words: Wolff's Law. Wolff's Law states that bone will adapt to the stresses placed upon it. The more stress, the more the bone will grow. The lower the stress, the less bone will grow. The bone that is particularly susceptible to becoming brittle and fracturing is called trabecular bone, or cancellous bone. Let's look at the anatomy for a moment. Trabeculae are bony projections within the bone that result in a matrix or lattice work that supports load bearing. The long bones of the body such as the humerus and femur have trabecular bone in the ends where the load is particularly important, for example the shoulder and hip. The vertebrae of the spine also contain trabecular bone. While the cortex of the bone, the outer wall, is also thick in the ends of long bones due to load bearing, trabeculae provide even more support for tension or compression forces in the bone. Think of them as little columns or buttresses supporting the large outer walls. These structures are the first to go with OP and literally make the trabecular bone disappear. Without this extra support fragility fractures are highly likely. Weight bearing activity and resistance training places stress upon the bone and results in bone building that can protect from losing bone density over time. Even if you already have OP when you start exercising, these types of exercises will still help to prevent fractures. Reason 2: Preventing Falls As we age our muscle tissue will slowly deteriorate if nothing is done to prevent it. Last week, we discussed sarcopenia, or progressive muscle tissue loss, as a preventable disease of advanced age. Preserving muscle strength is not only important for bone health, as the bone at the musculotendinous junction is thickened by the pull of muscle placed upon it, but also just as important for preventing onset of weakness in the lower body and trunk. This weakness results in poor balance reactions to prevent falls and inability to stop fall once a loss of balance occurs. Falls are a source of many of the fractures that occur with OP. Remember the statisic we saw earlier about 80% of fractures in the aging adult being the result of OP? If we can prevent the falls that lead to the fractures through exercise we can also prevent the loss of bone mineral density that leads to OP at the same time. 1 in 4 adults over the age of 65 will fall in 2018. How many will break a hip or a wrist, even a vertebrae? How many will not return home after they fall? Our easy chairs are more deadly than most people realize. It's time to get moving! What Exercises Are Safe with Osteoporosis? As a physical therapist, exercise prescription is a daily part of my job. With aging adults this takes more skill and adaptation. There are many ways to strengthen the muscles and to preserve flexibility without stressing the spine in a dangerous way. This is where a PT is so valuable and why we need to be training more people that are not therapists in exercise programs that encourage bone health without danger of fractures. There are programs out there that are very valuable that I will provide links to below. The guidelines of the ACSM state the following for recommendation of exercise for people with OP: Frequency: Weight bearing aerobics 3-5x/wk (if not daily) and resistance training 2-3 days per week Intensity: For aerobics, moderate exercise starting at 40% and working up to 60-80% of heart rate reserve. For resistance training, moderate intensity at 10-13 on Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion and 60-80% of 1 rep maximum. Time: 30-60 minutes total each day of exercise Type: Weight bearing aerobics such as walking, jogging, or elliptical. Water aerobics also valuable. Resistance training with bands, weight machines, or anti-gravity with supervision of a physical therapist. Here is what to look out for ->
At Hyland Physical Therapy and Wellness we are developing an exercise class for people with osteoporosis that is based upon the guidelines we have discussed today. This would be available in group format, but at any point I am available to consult with you individually to develop a safe program specifically for you. Contact me today to find out more. The links below will help you to get in touch with me. Sarcopenia... What the heck is that?!" I can hear you ask. I admit that it is not a very widely known term; however, it is in fact an actual medical diagnosis that is becoming more and more recognized. Sarcopenia is such a new concept that it is not even recognized in some countries. In Australia for example, medical schools are not even discussing this diagnosis, despite the fact that 30-40 per cent of those over 65 in Australia are likely affected with this disease. This is according to an article about sarcopenia that was just published this month in The Sydney Morning Herald. I found this to be extremely interesting when considering that falls are a geriatric issue discussed the world over, by the World Health Organization no less. Yet, a disease process that is resulting in falls, injury, death, and disability for aging adults is not even recognized across the globe!! WOW. The good news is that by gaining more and more recognition in the US, perhaps we can lead the way in prevention. The full article I am referring to can be found by clicking this link or copying to your web browser: www.smh.com.au/national/the-big-new-disease-that-doesn-t-officially-exist-in-australia-20180702-p4zp11.html?btis
So, what is it anyway? WARNING: We are about to get "sciency" here. Let the inner geek in you breathe a little. It won't hurt, I promise... According to the article cited above, an American scientist named Irwin H. Rosenburg coined the name sarcopenia in the 1980s. He invented the term by combining the Greek words sarco meaning "flesh" and penia, meaning "loss." The hallmark of the disease is a progressive loss of muscle mass through the decades. Here are some facts from research regarding sarcopenia:
What causes this phenomenon? As we mentioned earlier, lack of physical activity is the number one cause. As a natural part of aging sexual hormones decline, cell death rates increase, and the efficiency of mitochondrial function (contain cellular DNA and produces ATP, the power source of all organ functions) becomes impaired. This results in changes to the muscle tissue and the bones. Without physical activity this will be an accelerated decline. Another very important factor to consider is nutrition and absorption. If one's diet is deficient in protein, and without certain supplements such as Vitamin D, there will be nothing for the body to use to build up muscle tissue. When combined with a protein efficient diet, physical activity can actually aid in protein synthesis, as evidence indicates that the mechanical load placed on the muscle cells through exercise directly enables the muscle cell membrane's ability to synthesize protein (Narici et al, 2006). In summary, sarcopenia is a highly likely condition past the age of 50 and has been found to increase mortality independent of age and other disease processes. Physical activity and exercise is the means to prevent this condition from rearing it's ugly head. My mission is to help as many people as possible to prevent this condition and to age successfully. The paradigm shift that is needed is to move from failure to frailty to function to fun. Remember, the deadliest object in your home is your favorite comfy chair. In the United States, they have loved many of us to an early death. Plantar Fasciitis, or plantar fibromatosis, is a foot condition that is characterized by heel pain that can extend into the arch of the foot. It is normally worse first thing in the morning upon standing, and can also increase after prolonged standing throughout the day. An increase in standing activity prior to the start of the pain is typical, i.e., you started a new job where you were on your feet for hours on end on a concrete floor, etc. Weight can be an issue with this condition, though this is not thought to be a causative factor. One thing to note is that in 75% of cases the foot is a normal type, rather than high arches, collapsed arches, etc. Whatever the cause and whatever age it hits you, it can cause your exercise routine to come to a grinding halt. It hurts that much. In some cases osteophytes, or bone spurs, can form where the plantar fascia attach to the calcaneus bone in the heel. I wanted to address this topic due to the fact that plantar fasciitis, like many conditions out there, is not often addressed by a physical therapist. More often the individual sees their orthopedic physician or a podiatrist and is prescribed orthotics, resting night splints, and often corticosteriod injections. None of these treatments is wrong, but why is physical therapy not part of the recommended treatment? As we dive into this topic, I wanted to recommend some general advice for those suffering with plantar fasciits, but also to point to the evidence that physical therapy should always be included when trying to deal with this problem. Tissue changes that occur and result in this condition did not happen overnight and skilled physical therapy is needed to improve the tissue impairments that resulted in the pain condition. In 2014 a clinical practice guideline (CPG) for treating plantar fasciitis was published in the Journal of Orthopedic and Sports Physical Therapy (JOSPT). You may not be able to access this free without a membership, but the link to the full text article is here. In this CPG, the strongest evidence suggests that the best interventions for plantar fasciitis are a combination of manual therapy, specific stretching, taping, custom orthotics/inserts, and night splints. These received an A (strong evidence) by the reviewers for best evidence. Among the poorest evidence? It's what you might expect (or at least what I would expect): ultrasound, E-stim, phonophoresis, iontophoresis, etc. These received a C for evidence, which correlates to weak evidence. Knowing this, will you be satisfied with just receiving treatments that have the least evidence for success? With this knowledge, it should be apparent that physical therapy is needed with plantar fasciitis and is an imperative part of the management of this issue. The caveat to this statement is that physical therapy that emphasizes the techniques with best evidence is the only physical therapy worth pursuing. Beware of the classical approach of physical agents such as ultrasound, E-stim, etc. as these modalities can aid in some relief, but only temporarily. We want real tissue changes here and we also want improved function. A few months ago, I ran across a great infographic that was shared through the Academy of Geriatric Physical Therapy. I will link you to this post here. This is a fantastic summary of what a home exercise regimen should look like when self-treating plantar fasciitis, because it addresses flexibility of the ankle and calf muscles, maximally stretches the plantar fascia, and also addresses load shifting away from the medial portion of the foot with the shoe insert. I liked that the infographic emphasized that with the shoe insert you aren't changing position or biomechanics, but rather alleviating the load and stress off of the sensitive and overloaded tissue. I would argue that manual therapy to improve the pliability of the tissues (flexibility and ability to stretch) is crucial and therefore a PT is needed for this hands-on treatment in addition to the self-help exercises. It should be noted that the evidence cited in the CPG above only supports short term relief of the pain with stretches and exercises. For long term relief you will need manual therapy techniques as well as proper footwear. The point is, if plantar fasciitis has taken the fun out of your daily routine and you have been instructed to stop activities that you previously enjoyed, it's time to try to go back to what you enjoy. Reach out to a physical therapist to help you address this issue alongside your current treatment. Chances are, if it isn't getting any better, the approach is incomplete. Call today or fill out the contact form below and we will get in touch with you.
There are many physical conditions that could be a barrier to exercise — that is, unless you know a skilled exercise expert who can guide you along the way. This topic of barriers to exercise is very important to me, and I am passionate about empowering people to be as physically active and fit as possible, even with chronic illnesses. This will be a continued series for the next few months as we dive into various perceived, or in some cases actual barriers to fitness and active lifestyle. Does exercise take your breath away? Actually, in this case I mean in the literal sense. For this first installment I want to address respiratory problems. In general, respiratory diseases fall into two categories: obstructive and restrictive.
​Obstructive respiratory diseases that are more common in the population are asthma, COPD, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis. For the purposes of exercise prescription, I will focus on asthma and COPD and the implications for exercise. It is certainly possible to exercise safely and effectively with either condition. Asthma Asthma is an autoimmune condition that results in spasm in the large airways (bronchi) as well as increased mucous secretion. This results in blockage of the airway, thus the fact that it is an obstructive respiratory disorder. Asthma can make it difficult to breathe in or out and attacks can be triggered by high intensity exercise. For many this may seem impossible to deal with when trying to exercise, but by applying the FITT principle (Frequency, Intensity, Time, and Type) it is possible to progress to more intense exercise with the guidance of a physical therapist. As a general example: Frequency: 3-5 days per week Intensity: 30-40% of maximum heart rate (light) working up to 60-80% of maximum heart rate (high intensity/vigorous). Time: 20-60 minutes per day (either continuous or intermittent) Type: Walking or stationary cycling Calculating your heart rate maximum and percentages is a topic for another time, but suffice it to say that with such a guideline you will likely improve control of your asthma and decrease risk of hospitalization. Another alternative to cycling and walking is swimming, which is also cardiovascular exercise. Some considerations for exercise with asthma: 1. Do not attempt an unsupervised exercise regimen without the expertise of a physical therapist. Developing an individualized exercise prescription that is safe depends upon your individual vital signs and monitored response to exercise. 2. Always have your rescue inhaler with you, even if exercise has not provoked an attack. 3. Minimize the chance of bronchospasm (asthma attack) by choosing a safe environment for exercise. If you are prone to allergies, don’t walk or jog outdoors, at least not at first. Indoor tracks or even inside of your home could be safer. Also, some pools have a high chlorine content, which can induce attack. Pools that are salinated (salt water) are good and pools designed for aquatic physical therapy are even better due to the fact that they are kept above body temperature (typically around 100 degrees F) and the space is kept humid and warm, which can aid in keeping airways open and relaxed. COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or COPD, is typically associated with tobacco abuse and results in air becoming trapped inside the lungs when exhaling due to blockage of the airways with secretions and constricted bronchi. Due to the air being trapped in the lungs, gas exchange becomes imbalanced resulting in increased CO2 in the bloodstream. If left unchecked, hypoxia, or too little O2 saturation in the blood, can result and present a medical emergency. That may sound a bit scary, but safe exercise is possible with COPD. In fact, there are huge benefits. One example of clinical research in this area comes from Ferreira, et al in 2009 where they cite the benefits found in a simple walking program. The program was conducted three (3) days per week for twenty (20) minutes for a total of two (2) months. The results they found were:
A similar exercise prescription to asthma would be effective. Even if wearing supplemental oxygen, a monitored exercise program can still be developed and have positive results. Interval training has also been found to be very effective for COPD. Interval training involves combinations of different exercises such as warm up stretches/light walking, followed by upper body and lower body resistance exercises, then cool down. Typically rest periods last as long as the exercise, so for example, a typical interval session might look like warming up by walking for 1 minute, stretch for 1 minute, then doing 20 mini squats, then fast walking for 1 minute, then resting for 1 minute, etc. With COPD the exercises are usually of shorter duration and also have a 1:1 ratio of rest to exercise. For a client with COPD (as an example), I would likely recommend 30 seconds of walking at regular pace, followed by 30 seconds rest, then 30 seconds of marching in place, 30 seconds rest, 30 seconds worth of mini squats, 30 seconds rest, etc and the following may be applied: Frequency: 3-4 days per week aerobic, 2-3 days per week strengthening Intensity: Light to moderate (30-60% max heart rate) and progress to 80% max heart rate for aerobics. 50-80% of 1 rep maximum for resistance/strengthening exercise Time: 15-20 minute sessions Type: Interval training (similar to above), resistance training for lower and upper body major muscle groups, aerobic exercise. Some considerations for exercise with COPD: 1. Again. Do not attempt an unsupervised exercise regimen without the expertise of a physical therapist. Developing an individualized exercise prescription that is safe depends upon your individual vital signs and monitored response to exercise. 2. Always time exercise for the peak times with your bronchodilator medication. That way you get the most bang for your buck in terms of ability to bring air in and out due to the airways being more open. 3. Stop smoking! Please. I’ll just leave it at that. For restrictive pulmonary diseases, the picture isn’t so rosy. These diseases include pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, etc. This results in inability to inspire enough air into the lungs due to lack of expansion. Hypoxia, chronic shortness of breath, and eventual decline in the function of the alveoli in the lungs (the small sacs that fill with air and exchange gases) make exercise extremely difficult, if not impossible, for some individuals. Many individuals will eventually need lung transplant or be placed on hospice for the long term. The main thing to consider is maintaining the best quality of life possible by maintaining an airway, promote adequate oxygenation, manage dyspnea, and to prescribe exercise with adequate rest periods for best tolerance of exercise. As an example, I have treated a gentleman that has ankylosing spondylitis, a skeletal condition resulting in spinal fusion and rib stiffness, as well as a new diagnosis of Amyotropic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease). He required the use of a machine to assist in his breathing while sleeping, and attached to supplemental oxygen, as well as elevation of the head of the bed while sleeping. Despite the impairments and restrictive respiratory issues, he was able to tolerate shorter sessions that involved walking with his walker for as far as tolerated, or bed exercises, or repeated sit to stand. Additions of any other exercises proved to be too much for him, but he was still able to tolerate activity each time and actually made some progress. For him, the goal was to stay as functional as possible for as long as possible, though ultimately his medical issues will eventually be terminal. This is to illustrate that it is still possible to exercise with such conditions. Overall, respiratory issues can be worked around to allow you to have an active lifestyle and improved quality of life. As a physical therapist certified in exercise prescription for aging adults, this is exactly what I can help people to do every day. So, take a deep breath, and let's get you moving! |
AuthorDr. Michael Hyland, DPT, CEEAA has been a physical therapist since 2012. He is a Certified Exercise Expert for the Aging Adult and an expert in Parkinson's Disease. He owns Hyland Physical Therapy and Wellness in Broken Arrow, OK Archives
October 2022
Categories
All
|
Proudly powered by Weebly














 RSS Feed
RSS Feed